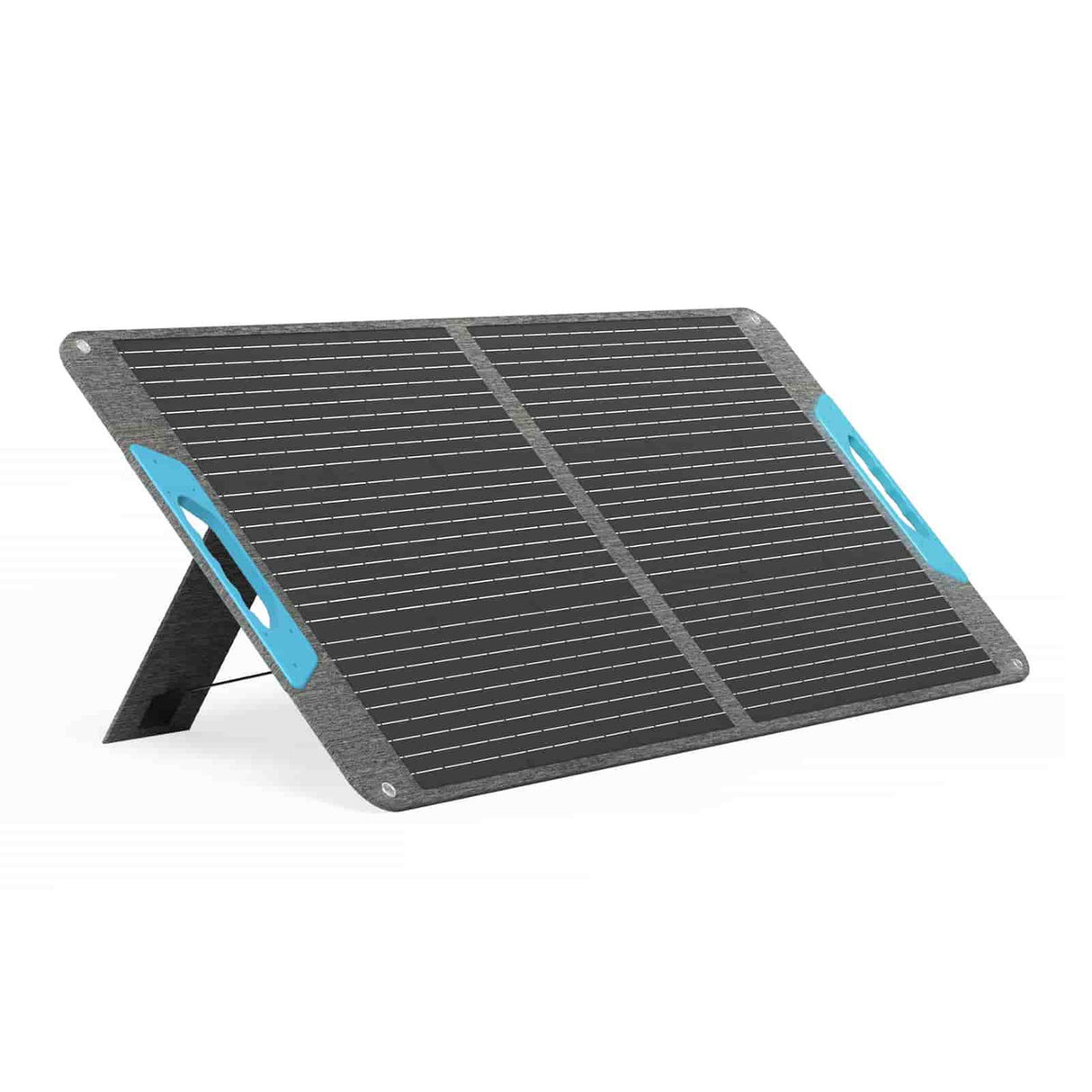
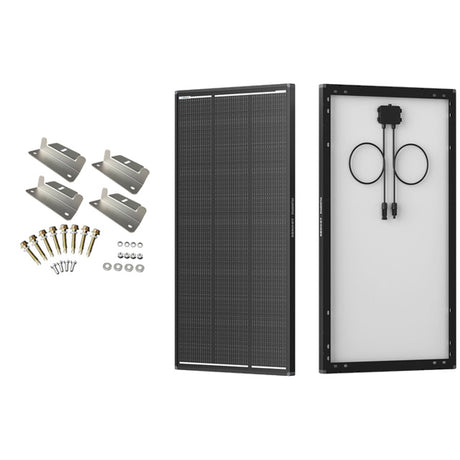
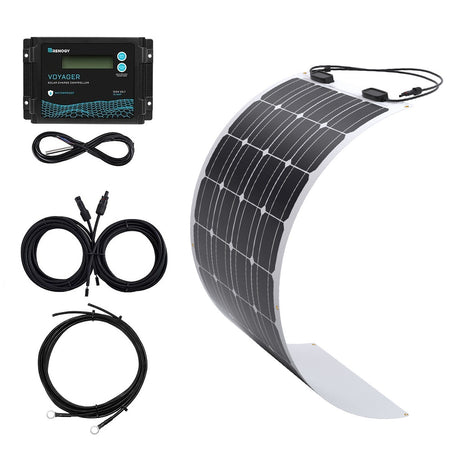
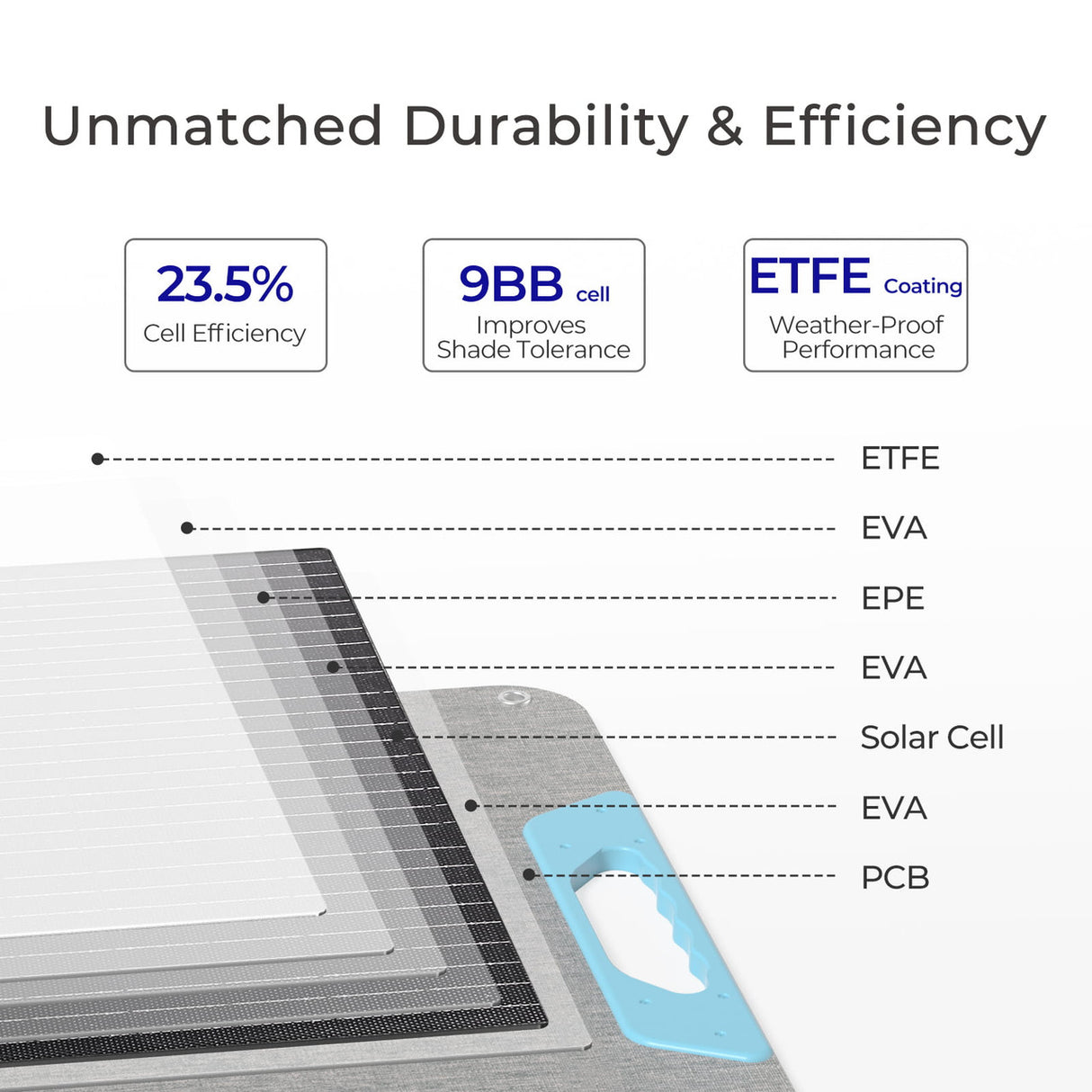
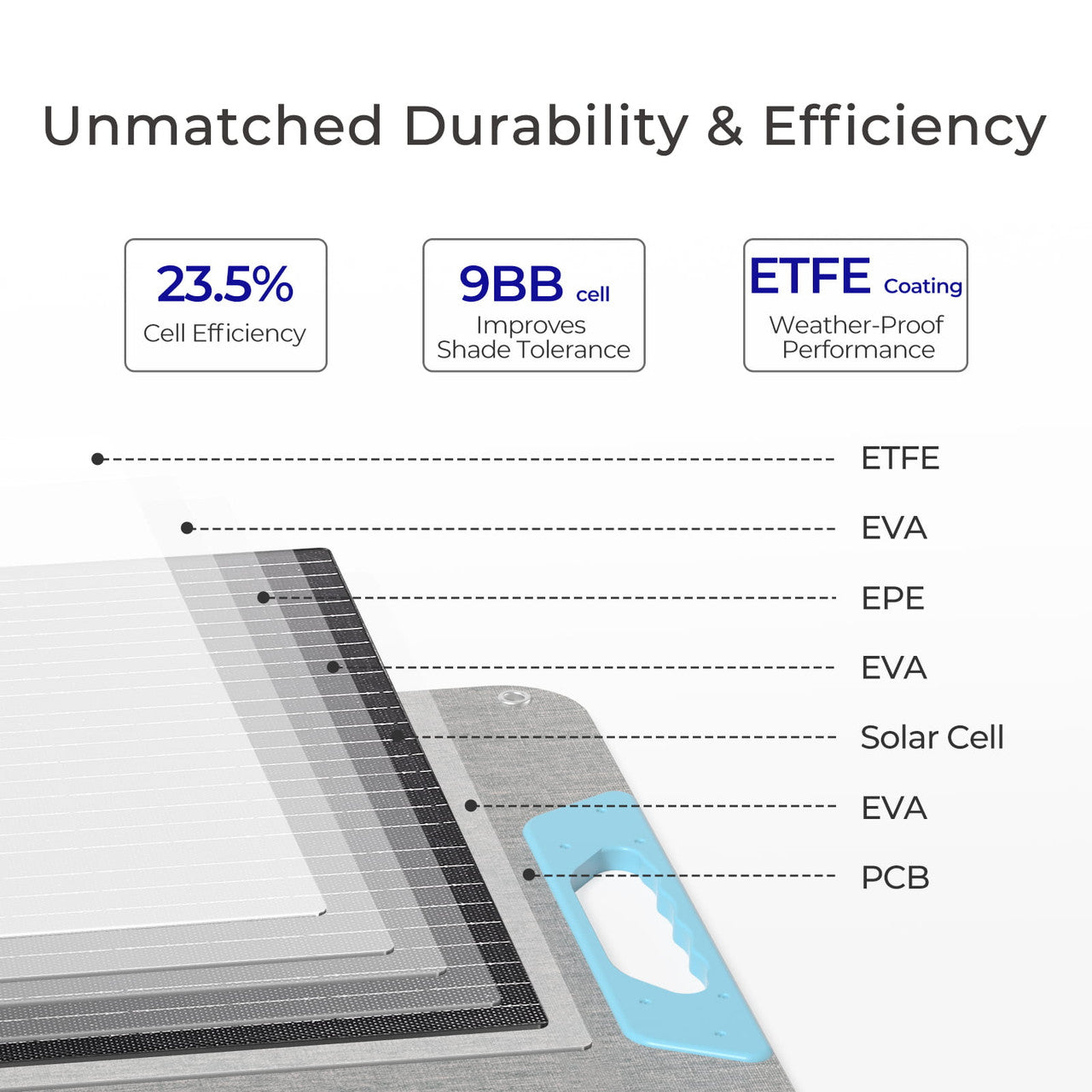
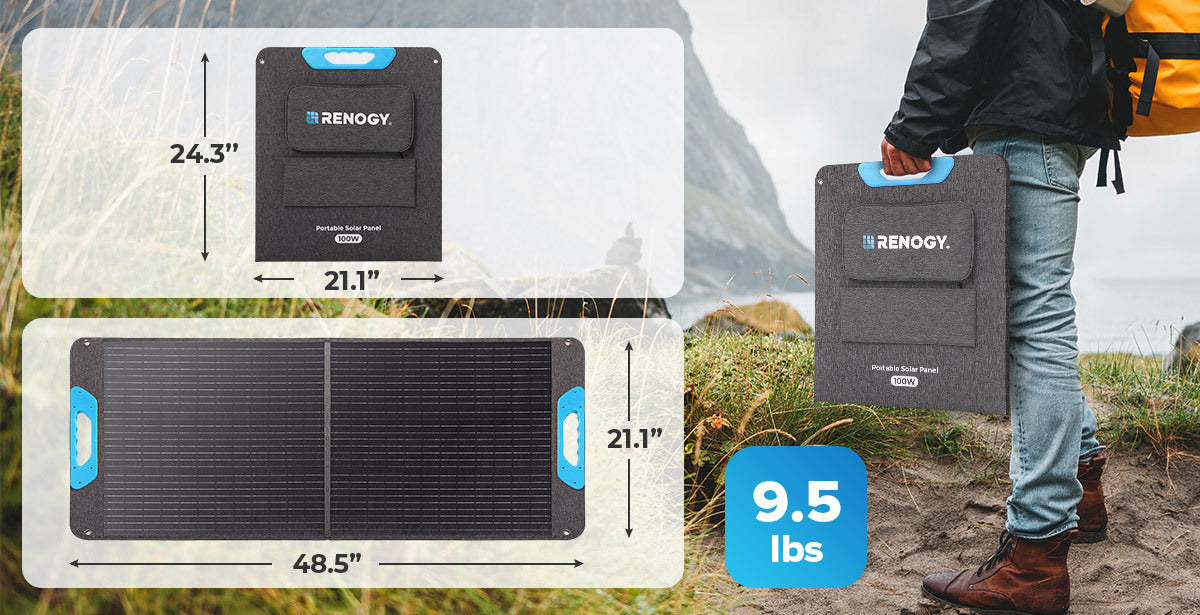
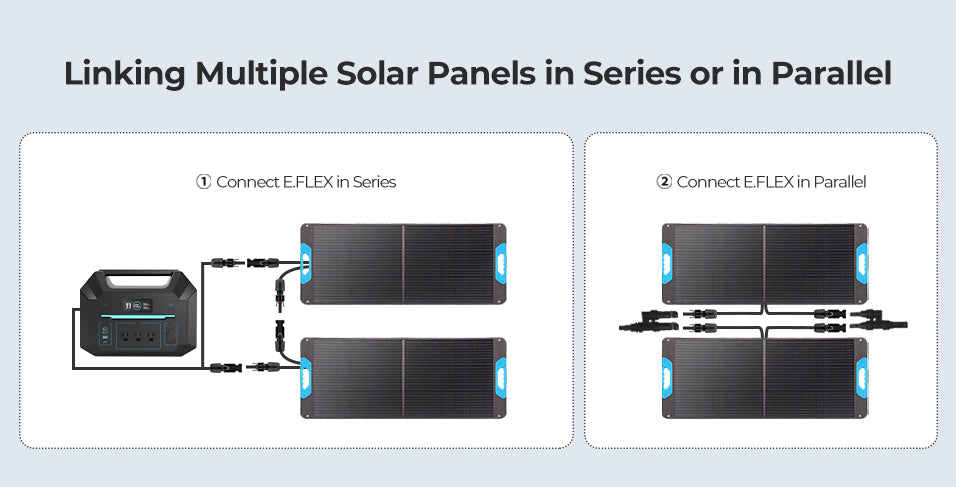
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Install a Solar Panel at Home
Solar power is an extremely affordable and sustainable way to run your small and energy-hungry home appliances, including bulbs, fans, microwave ovens, washing machines, and air conditioners. Solar energy offers...